SpaceX Starship Explosion Insights
Investigating the Explosion
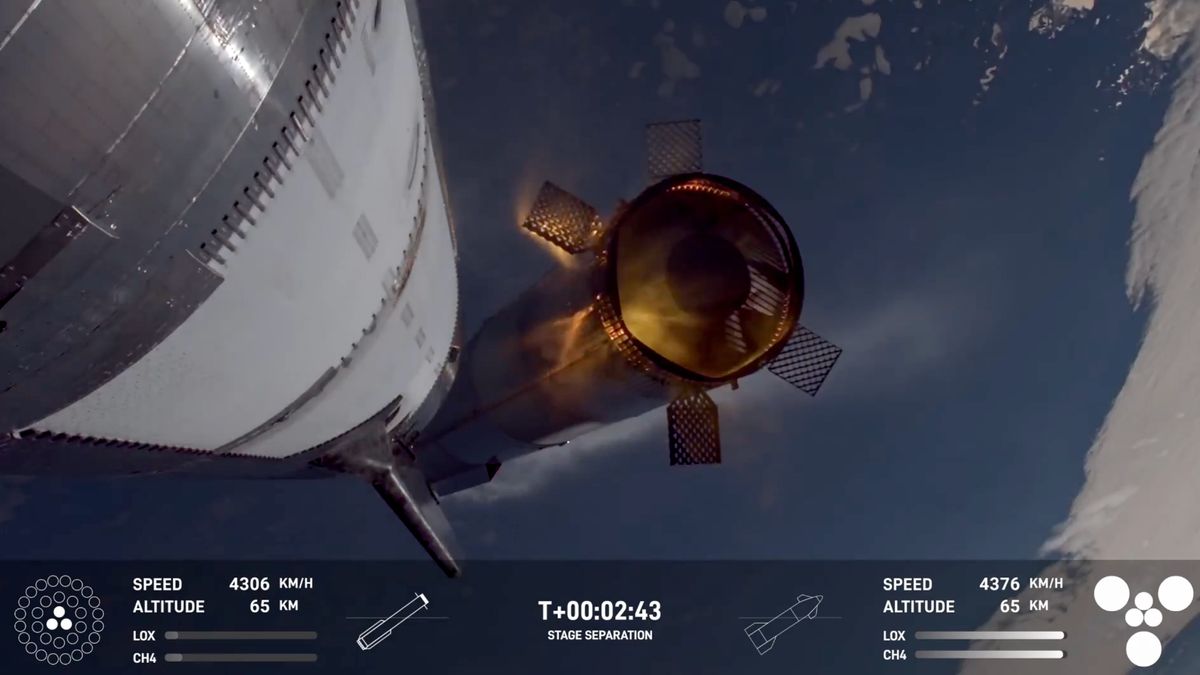
On January 16, SpaceX's Starship launch took a dramatic turn when the upper stage of the vehicle was destroyed in an explosion. Preliminary reports from SpaceX CEO Elon Musk suggest the incident was likely caused by a propellant leak. Musk noted, "Preliminary indication is that we had an oxygen/fuel leak in the cavity above the ship engine firewall that was large enough to build pressure in excess of the vent capacity." This insight suggests a critical flaw in the containment of fuel and oxidizer, prompting immediate investigations and redesign considerations.
The Role of Propellant Leaks in Rocket Failures
Propellant leaks have been a persistent challenge in rocketry due to the high pressure and volatile nature of the chemicals involved. When leaks occur, they can lead to catastrophic consequences. Lessons learned from this incident could drive future innovations in leak detection systems, materials engineering, and structural design to enhance safety protocols.
"Space is hard, but it's worth it. Every mistake fuels a thousand successes." - Elon Musk
Implications for Space Exploration
The explosion underscores the inherent risks involved in pioneering space travel. With Starship designed for ambitious missions to the Moon and Mars, ensuring the reliability of its components is paramount. This incident may influence timelines and strategies for NASA's Artemis program, which plans to utilize SpaceX's Starship for lunar missions.
For those interested in the development and safety of space technologies, these incidents offer valuable insights. You may want to explore books on SpaceX's engineering triumphs and challenges on Amazon.
The Future of SpaceX Post-Incident
Despite setbacks, SpaceX is well-acquainted with turning failures into opportunities. This event is expected to accelerate enhancements in technology and protocols. The drive to conquer space will continue, echoing the sentiments of pioneers like Elon Musk and resonating with space enthusiasts worldwide.
- Enhanced safety mechanisms for future missions
- Redesign considerations based on incident data
- Innovative material and structural solutions
